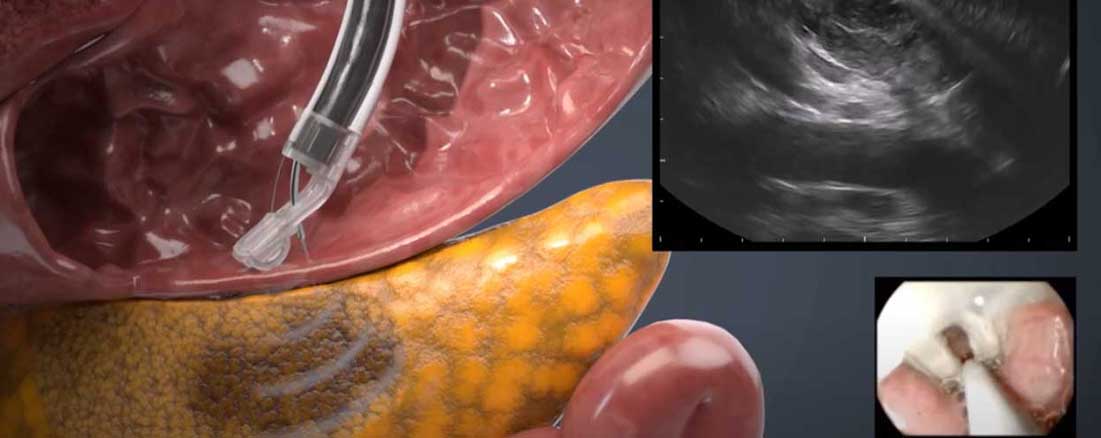
What is it?
An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a medical procedure that combines both ultrasound imaging and endoscopy. This is used to examine the digestive tract and surrounding organs of a patient.
Endoscopic ultrasounds have been a valuable diagnostic and therapeutic tool in gastroenterology, but it is traditionally performed exclusively in hospitals because of the high cost and technical requirements. EndoSound Vision System™ (EVS™) is changing that! With EVS™, access to advanced EUS technology is more obtainable throughout smaller hospitals, surgical centers, advanced clinics and more, at a fraction of the cost.